MK5GC
Short Description:
The MK5GC product is a lightweight 5G core network product based on the 3GPP standard protocol. The product uses the SBA microservice architecture to achieve a complete decoupling of network element(NE) functions and hardware functions, and can be deployed on a variety of cloud and x86 servers. MK5GC can help private network users to build the 5G core network quickly, flexibly and efficiently at a very low cost, meet various application scenarios of private network users, and help private network users to digitize and transform intelligently.
Product Detail
Product Tags
Introduction
Product Introduction
The MK5GC product is a lightweight 5G core network product based on the 3GPP standard protocol. The product uses the SBA microservice architecture to achieve a complete decoupling of network element(NE) functions and hardware functions, and can be deployed on a variety of cloud and x86 servers. MK5GC can help private network users to build the 5G core network quickly, flexibly and efficiently at a very low cost, meet various application scenarios of private network users, and help private network users to digitize and transform intelligently.
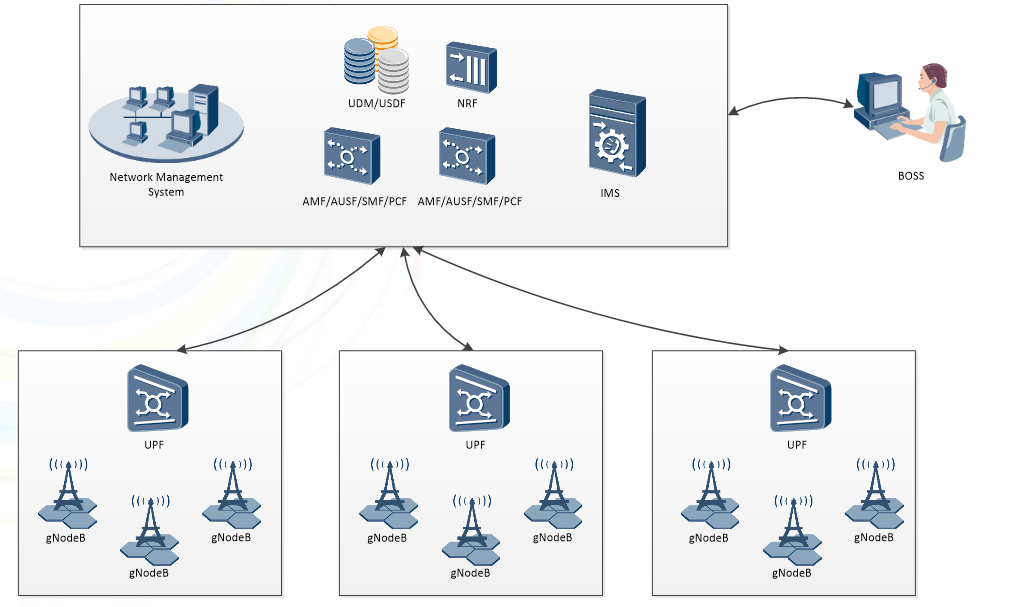
The currently supported network architecture is shown in the figure below:
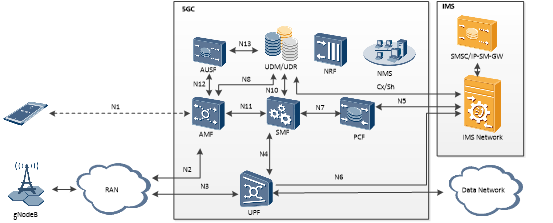
Figure 1 Architecture diagram of the MK5GC system
All the interfaces between the network elements are implemented in strict accordance with the 3 GPP standard.
Functional description
Product features and business functions
Product characteristics
• The SBA microservice architecture based on 3GPP
• The cloud virtualization container deployment can be used
• SA independent networking
• CU separation
• Support network slicing
• Supports both centralized and distributed deployment
• Support for network function sinking
• Support switching
• Support voice VoNR, short message
Business function
➢ Control surface: 5G authentication encryption and decryption, registration, de-registration, paging, business request, An release, user information management, mobility restriction, area limit, session establishment, modification and release, UPF selection, switching, voice and short messages.
➢ Data surface: support three-layer and four-layer package identification and rule forwarding, gating and QoS-based flow control, PFCP session management, usage reporting and statistics and other functions.
➢ Support interface Based on the 3GPP standard support,
N1 / N2 / N3 / N4 / N5 / N6 / N7 / N8 / N9 / N10 / N11 / N12 / N13 / N14 / N15 / N22 / N26, Supports SBI-based servitization interface, which can meet the independent or joint deployment of each network element.
Detailed list of functions
|
function |
subfunction |
description |
Whether support or not |
|
Service |
Service registration |
support |
|
|
Service deregistration |
support |
||
|
Service discovery |
support |
||
|
Service update |
support |
||
|
Service authorization |
support |
||
|
Service status subscription notification |
support |
||
|
communications security |
AMF |
User identity privacy |
support |
| 5 GAKA certification |
support |
||
| UE registration exception without contracted 5G business |
support |
||
| NAS for protection against replay |
support |
||
| Downdegradation protection for Xn switching |
support |
||
| N2 Switching/moving registration Updates the NAS protection algorithm selection changed by the AMF |
support |
||
| Invalid or unacceptable UE security capability handling |
support |
||
| The NAS security mode, integrity, and encryption protection |
support |
||
| Switch between the secret key and the algorithm negotiation |
support |
||
| Access authentication and abnormal support |
support |
||
| 5G GUTI Redistribution |
support |
||
|
SMF |
User interface security policy priority |
support |
|
| The SMF checks the user interface security policy in Xn switching |
support |
||
|
UPF |
N3 interface user data confidentiality protection |
support |
|
| N3 interface user data integrity protection |
support |
||
| N3 interface user data against replay protection |
support |
||
| User data protection of N9 interface in PLMN |
support |
||
| N4 interface for signaling data protection |
support |
||
|
Connectivity, registration, and mobility management |
Sign up / go to register |
UE Initial Registration (SUCI) |
support |
| UE Initial Registration (5G-GUTI) |
support |
||
| Mobility registration updates |
support |
||
| Periodic registration |
support |
||
| The UE initiates a normal deregistration |
support |
||
| The UE initiates a shutdown deregistration |
support |
||
| The AMF initiates the deregistration |
support |
||
| The UDM initiates the deregistration |
support |
||
| Implicit deregistration |
support |
||
|
Service request |
A UE initiated business request, idle state |
support |
|
| A UE initiated business request, connection state |
support |
||
| There is downlink data on the network side, triggering a service request |
support |
||
| There is a downlink signaling on the network side, triggering a service request |
support |
||
|
AN release process |
The AN release flow initiated by the RAN |
support |
|
| The AN release flow initiated by the AMF |
support |
||
|
User information management |
Signing information update notification AMF |
support |
|
| Signing information update notification SMF |
support |
||
| The AMF initiates the Purge process |
support |
||
|
Configuration update |
AMF initiates the AMF configuration update |
support |
|
| AMF initiates the UE initiate configuration update |
support |
||
|
Restrictions on mobility |
RAT restriction |
support |
|
| Forbidden zone restriction |
support |
||
| Service Area restriction |
support |
||
|
Accessibility management |
UE reachability management in idle state |
support |
|
| MICO mode |
support |
||
|
session management |
Session establishment |
UE initiated session build, supporting v4 / v6 / v4v6 |
support |
|
Session modification |
The PDU session modification |
support |
|
| The UDM initiated PDU session changes |
support |
||
| The PCF initiated PDU session changes |
support |
||
|
Session release |
The UE initiated session release |
support |
|
| Session release initiated on the network side |
support |
||
|
SSC mode |
The PDC session anchor redirecting process for SSC mode 2 |
support |
|
| The PDU session anchor redirecting process for Multiple PDU session SSC mode 3 |
support |
||
| The PDU session anchor redirecting process for IPV6 multi-homing mode SSC mode 3 |
support |
||
|
ULCL uplink diversion |
Add joint PDU session anchor points and ULCL branch points |
support |
|
| Remove joint PDU session anchor and ULCL branch point |
support |
||
| Modify joint ULCL and PDU session anchors |
support |
||
| Add separate PDU session anchors points and ULCL branch points |
support |
||
| Remove separate PDU session anchor points and ULCL branch points |
support |
||
| Modify separate PDU session anchors points and ULCL branch points |
support |
||
|
LADN function |
Local data network session establishment |
support |
|
| Session release triggered by the UE leaving the local network service area |
support |
||
| PDU session user interface connection deactivation triggered by the UE leaving the local data network service area |
support |
||
|
PDU session user interface to activate |
support |
||
|
switching |
Xn switching |
Xn switching, no reelecting UPF |
support |
| Xn switching, inserting the I-UPF |
support |
||
| Xn switching, reelect I-UPF |
support |
||
|
N2 switching |
N2 switching, no reelecting UPF |
support |
|
| N2 switching, reelecting I-UPF |
support |
||
| N2 switching, reelecting AMF |
support |
||
|
4G/5G interoperability |
4G/5G switch |
5G to 4G |
support |
|
position message |
Location report process |
support |
|
|
strategy control |
AM strategy control |
Establishment of the AM policy associations |
support |
| Modification of the AM policy associations |
support |
||
| End of the AM policy association |
support |
||
|
SM strategy control |
Establishment of the SM policy associations |
support |
|
| Modification of the SM policy associations |
support |
||
| End of the SM policy association |
support |
||
|
Network slice |
Slice deployment |
support |
|
|
Slice deletion |
support |
||
|
Slice selection |
Selection of initial registered slices |
support |
|
| Redirection between AMF, according to the slice |
support |
||
| PDU session establishment initiation slice selection |
support |
||
| Configure the slices to be delivered to the new process |
support |
||
|
Data surface function |
Service identification and forwarding |
Three-tier rules identify and forward IPv4 |
support |
| Three-tier rules identify and forward IPv6 |
support |
||
| Four-layer rules identify and forward |
support |
||
| HTTP protocol identification |
support |
||
| DNS, FTP, and MQTT protocol identification |
support |
||
| URL discriminate |
support |
||
|
Service diversion |
Service diversion under the ULCL |
support |
|
| Service diversion under the Multi-homing |
support |
||
|
End marker |
Switch, UPF unchanging, UPF sends End marker packet according to SMF instructions |
support |
|
| Switch, UPF changing, UPF sends End marker packet according to SMF instructions |
support |
||
|
Data cache |
The UPF downlink data cache as indicated by the SMF |
support |
|
|
Strategy execution |
The UPF receives and performs the gating rules issued by the SMF |
support |
|
|
|
The UPF receives and performs the QoS rules issued by the SMF |
support |
|
|
N4 association |
N4 association establishment, update, release, and heartbeat detection |
support |
|
|
N4 session |
Establishment, update, and release of N4 sessions |
support |
|
|
Session-level reporting of the N4 interface |
Usage report |
support |
|
| Traffic detection report |
support |
||
| Idle-state data report |
support |
||
| PDU session activity reporting |
support |
||
|
Policy and billing controls |
Session management policy control |
The gating function |
support |
| QoS policy control and execution |
support |
||
| Qos Flow binding |
support |
||
| Session management policy modification initiated by the SMF |
support |
||
| Session management policy modification initiated by the PCF |
support |
||
| Session management policy termination initiated by the SMF |
support |
||
|
Access and mobility policy control |
Access and mobility policy establishment |
support |
|
| AMF initiated access and mobility policy modifications |
support |
||
| PCF initiated access and mobility policy modifications |
support |
||
| AMF initiated access and mobility policy termination |
support |
||
|
Billing control |
quotas administered |
support |
|
| Reporting based on traffic statistics |
support |
Network element management
Unified management of NE , can support NE configuration, query NE state, NE restart and other functions.
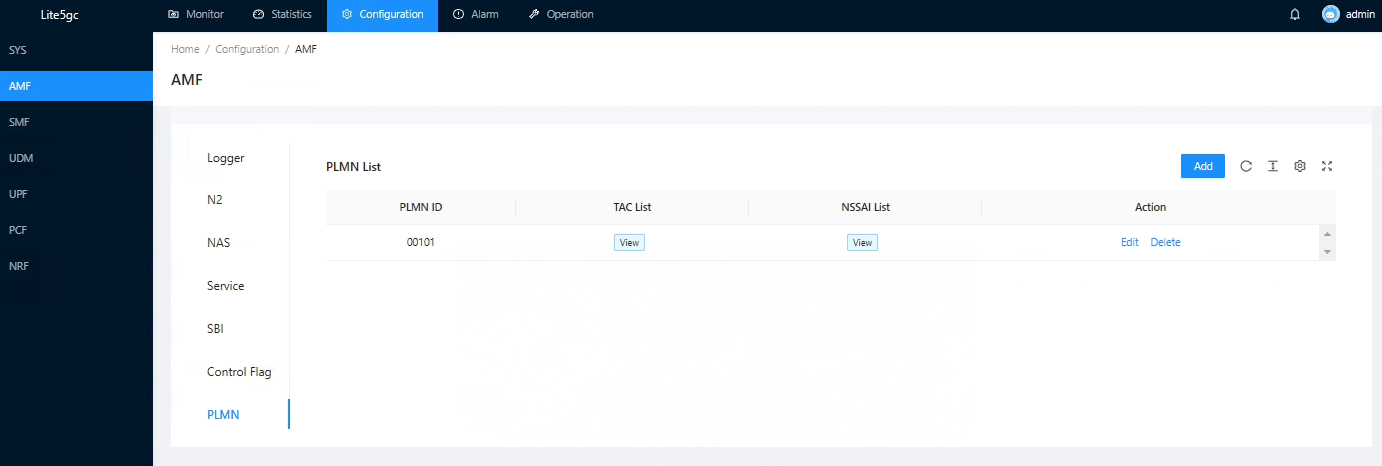
Figure 2 AMF NE configuration information
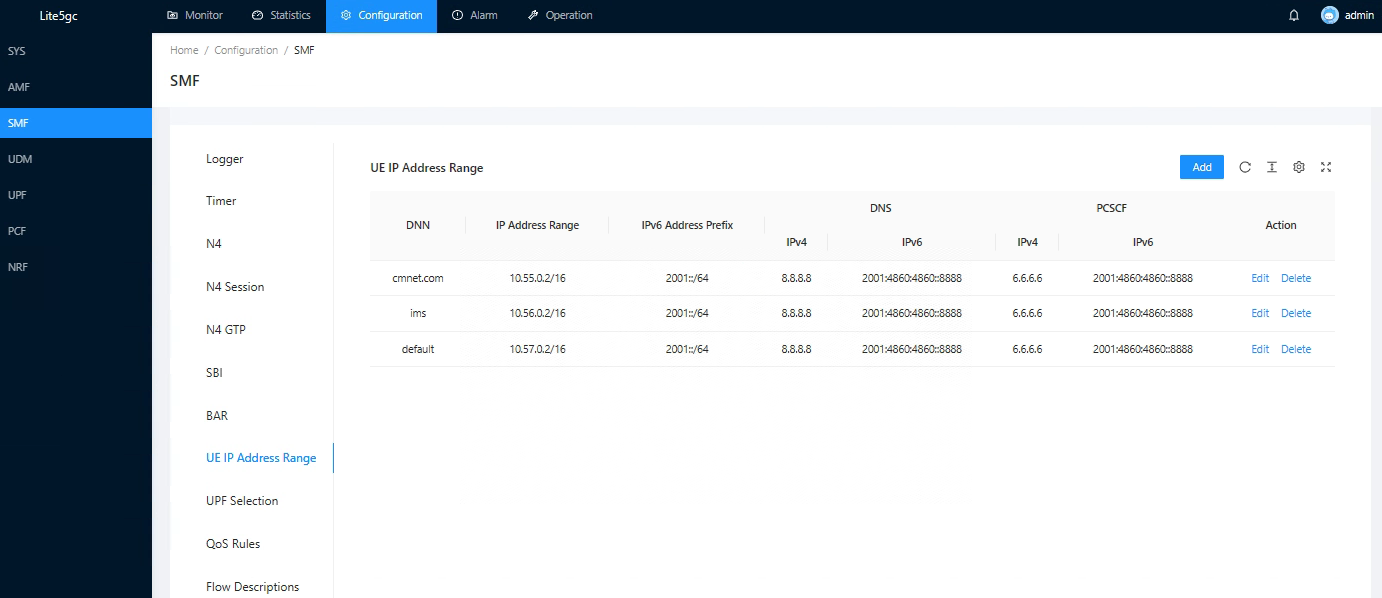
Figure 3 SMF NE configuration information
Figure 4 UDM NE configuration information
Figure 5 UPF NE configuration information
Figure 6 NE status display
It can monitor the number of online base stations and UE in real time, and pay attention to cpu, memory, disk and other conditions in real time.
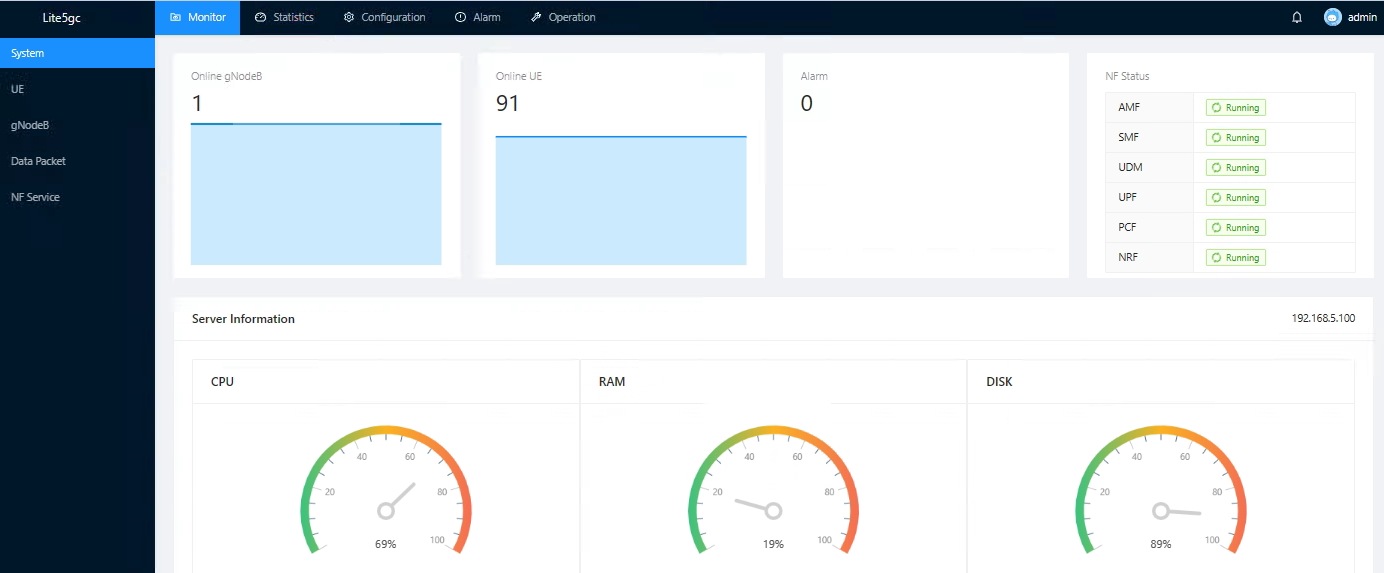
Figure 7. Real-time monitoring
The online UE situation and specific information can be viewed in real time.
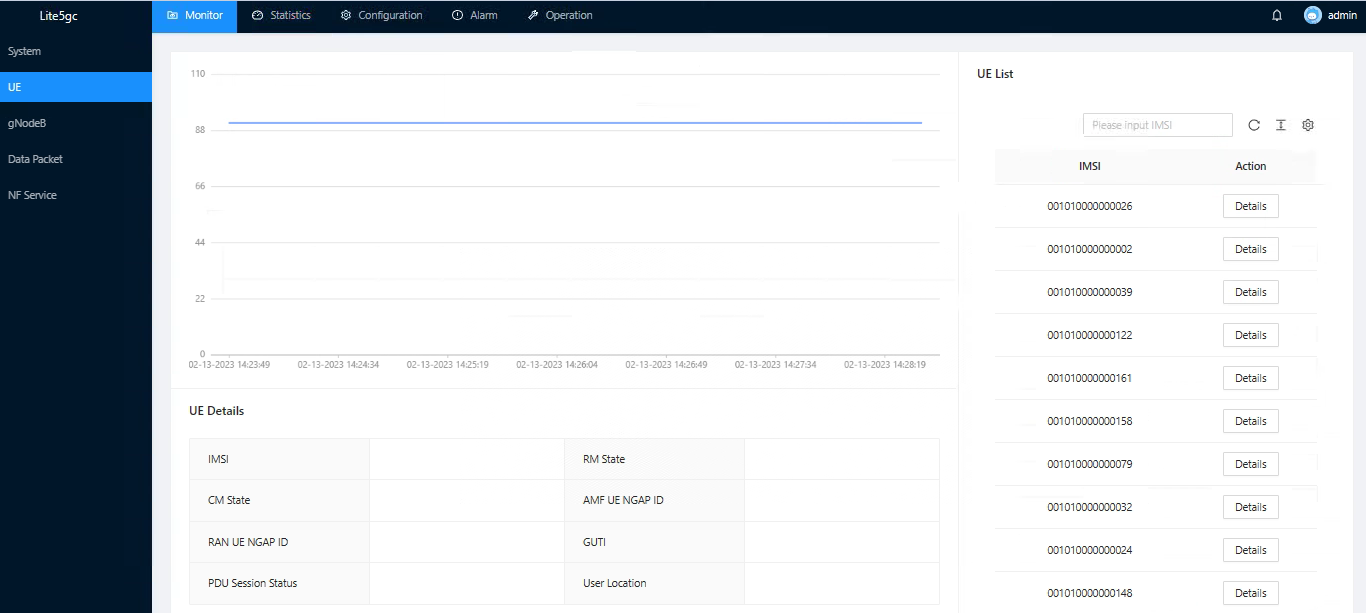
Figure 8. Online UE Information
Real-time view of the online base station situation and specific information.
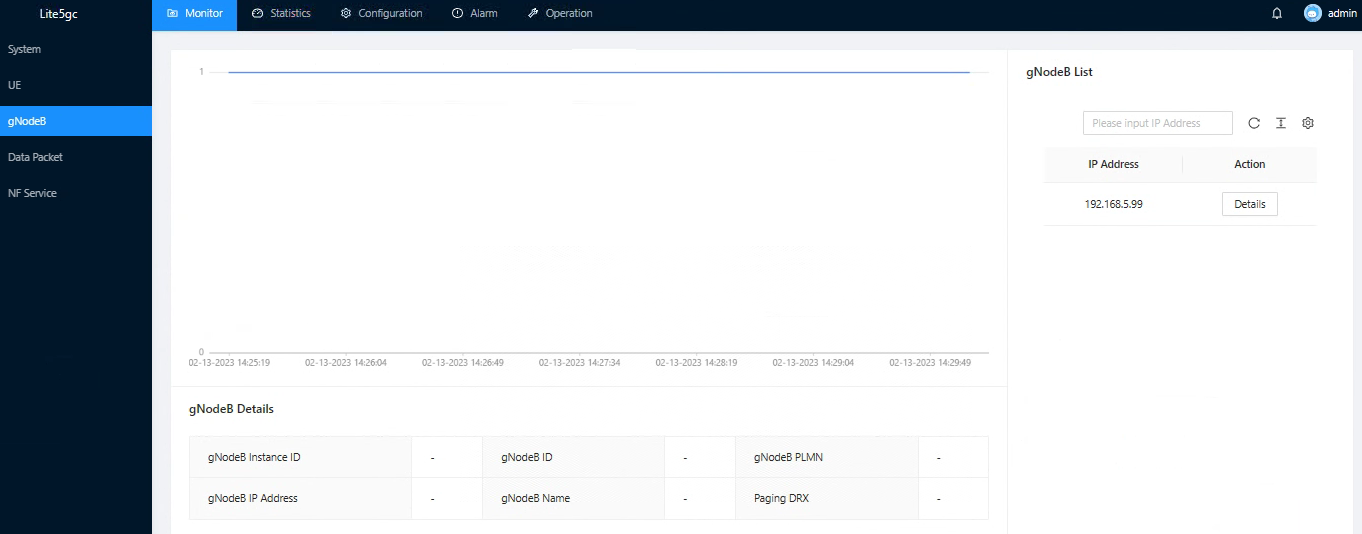
Figure 9. Online base station information
You can view the NE signaling statistics information.
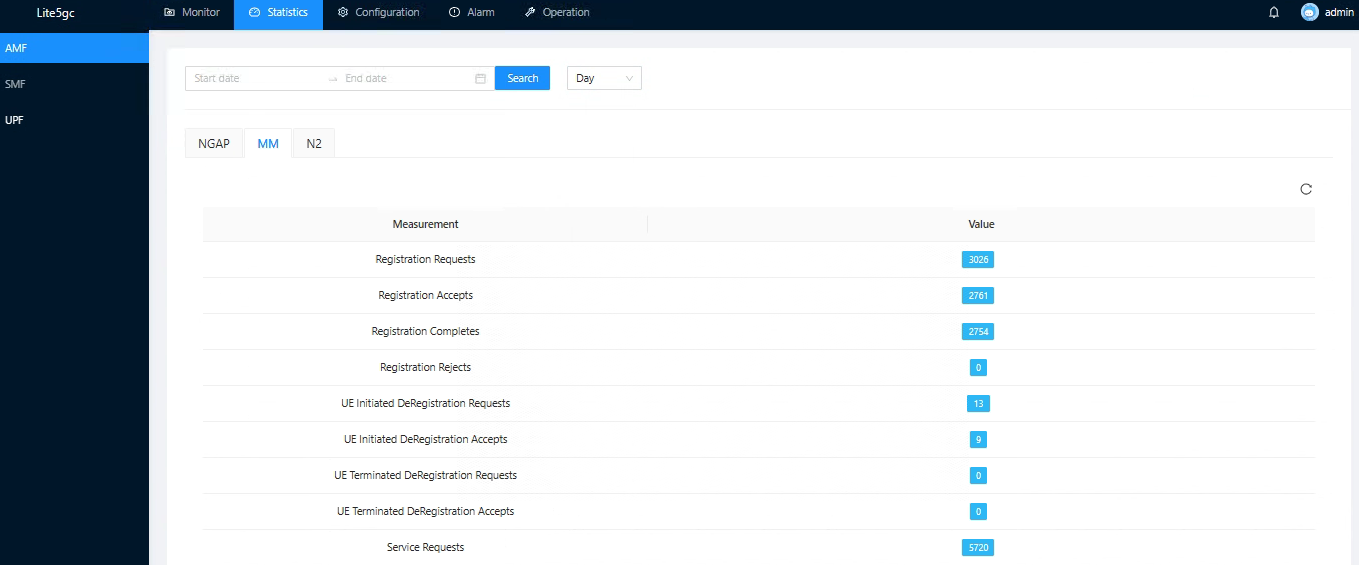
Figure 10 NE signaling statistics
You can view the flow statistics in real time.
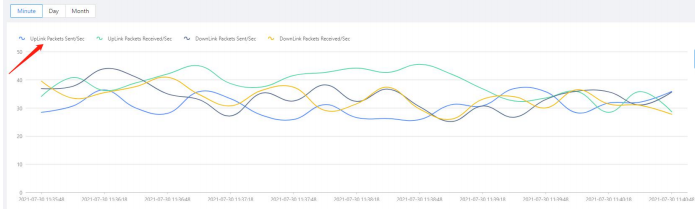
Figure 11 Flow statistics
Specifications
Lightweight core network currently has four specifications, the indicators are as follows.
Micro-sized 5GC products
|
Miniature 5GC |
|
|
Maximum number of connected base stations |
1-4 |
|
Maximum number of online users |
200 |
|
throughput of system |
1Gbps |
|
Virtualization / containerization |
Soft and hard integration |
|
1 + 1 main backup disaster recovery |
nonsupport |
|
Unified or stand-alone deployment |
unified |
|
Hardware specifications |
CPU 4-core 2.0G 8GB memory 256GB SSD, 4*1G NIC |
|
power |
Power supply power: 84W |
|
product size |
180×125×55 mm |
|
ambient temperature |
Applicable environment: storage temperature-20℃ ~70℃Operating temperature: -20℃ ~60℃
Storage humidity: -40℃ ~80℃ Working humidity: 5% -95% relative humidity, no condensation |

Figure 12 Hardware of micro-core products
Small-size 5GC products
|
Small 5GC |
|
|
Maximum number of connected base stations |
10 |
|
Maximum number of online users |
4000 |
|
throughput of system |
3Gbps |
|
Virtualization / containerization |
Soft and hard integration |
|
1 + 1 main backup disaster recovery |
nonsupport |
|
Unified or stand-alone deployment |
unified |
|
Hardware specifications |
CPU 20 Threads 2.1G 8GB memory 500GB SSD, 2*10G NIC,2*1G NIC |
|
power |
Power supply power: 250W |
|
ambient temperature |
Applicable environment: storage temperature-20℃ ~70℃Operating temperature: -10℃ ~60℃
Storage humidity: -40℃ ~80℃ Working humidity: 5% -95% relative humidity, no condensation |

Figure 13 Hardware of small 5GC products
Lightweight 5GC product
Depending on the hardware resources, there can be a variety of different specifications supported.
|
Lightweight 5GC |
|
|
Maximum number of connected base stations |
50 |
|
Maximum number of online users |
10,000 |
|
throughput of system |
15Gbps |
|
Virtualization / containerization |
support |
|
1 + 1 main backup disaster recovery |
support |
|
Unified or stand-alone deployment |
support |
|
Hardware specifications |
CPU 24 Threads 2.1G 16GB memory 500GB SSD, 2*25G NIC,2*1G NIC |
The hardware form can be a separate standard server, or a private data center virtualization deployment.

Figure 14 Standard universal server hardware
Standard 5GC product
Standard 5GC products can be deployed according to the actual requirements, such as virtual machines, containers, or servers.
|
Number of active users |
base number |
Data surface throughput |
Deployment mode |
Server or VM |
hardware requirements |
|
20K |
100 |
30Gbps |
Unified or distributed deployment |
1 unit / 2 VM |
36Core*2.2G, 32G memory, 2 * 1G, and 2 * 40 G NIC |
Product form
Support a variety of product forms, independent service deployment, virtualization deployment (virtual machine or container), cloud host deployment.
Flexible deployment according to customer needs and actual situation.
Interface standard development, can be customized according to customer needs, flexible to meet the actual needs of customers.

Networking scheme
➢ Centralized deployment mode, with small networks suitable for low-cost requirements.
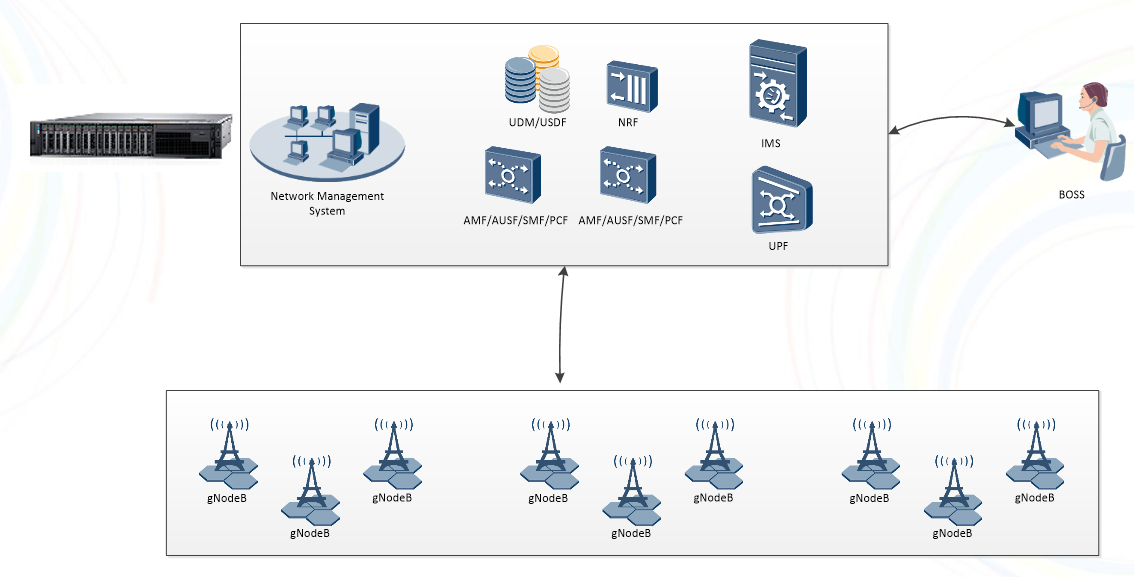
➢ Typical networking mode, suitable for small and medium-scale networks